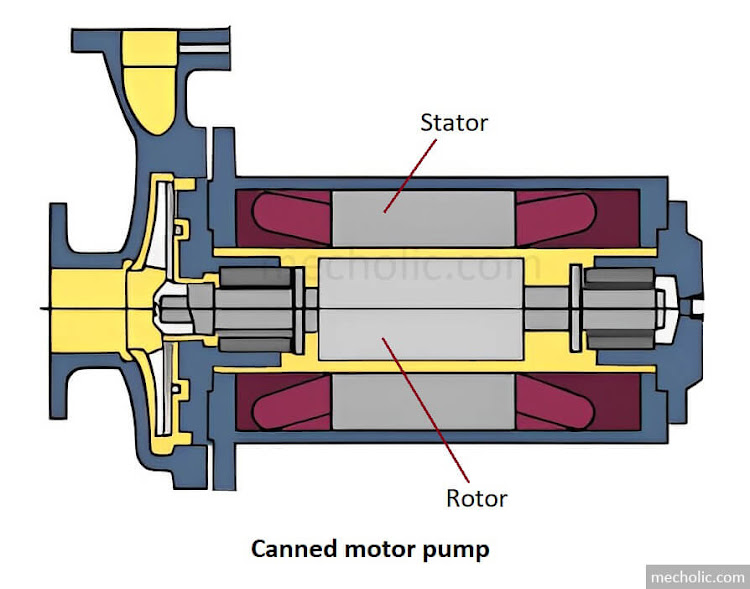
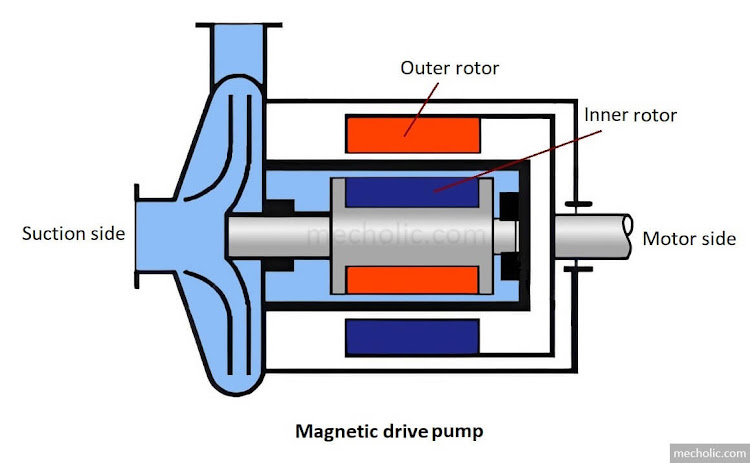
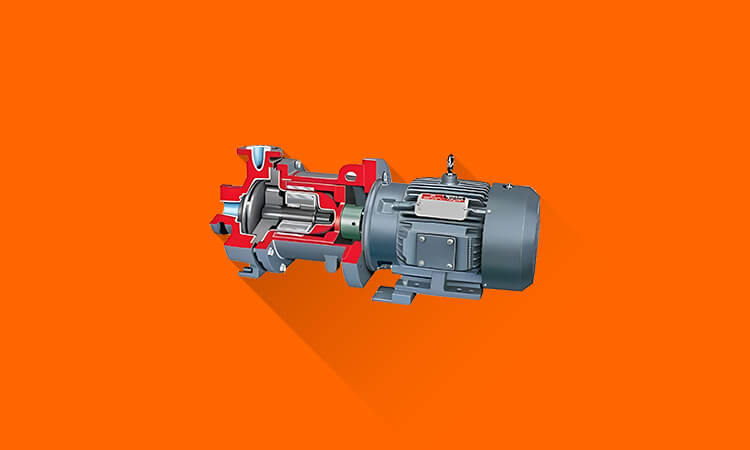
Hydraulic Intensifier Construction, Working Principle and Equation
Fluid Mechanics Hydraulic MachinesWhat is A Hydraulic Intensifier?
An intensifier or pressure booster is an internal power regenerator device used to increase fluid pressure, usually oil or water. Intensifiers may be either hydraulically or pneumatically operated, the advantage of the latter being that no power unit is required since the air can be taken from the general supply or storage tank. This hydraulic machine increases the intensity of pressure of a given liquid with the help of hydraulic energy of low-pressure liquid of large quantities. Such a device is needed when hydraulic machines such as hydraulic press require water at very high pressure, which cannot be obtained from the main supply directly. By means of an intensifier, it is possible to raise the intensity of pressure as high as 160 MN/m2



.jpg)